We are a global operator of essential infrastructure
- Renewable energies covered 32% of the demand
- Installed power capacity in the complete set of generating facilities on the peninsula grew by 2,356 MW
- 860 km of new line in the national transmission grid
Gross demand for electrical energy on the Spanish peninsula in 2012 was 252,191 GWh, 1.2% below that registered in 2011, according to the provisional data of the Spanish Electricity System Preliminary Report 2012. After factoring in the effects of seasonal and working patterns, consumption on the peninsula registered a fall of 1.7%.
The yearly maximum of instantaneous power demand was registered at 43,527 MW on 13 February at 8:21 pm.
The maximum demand value for average hourly power reached 43,010 MW between 8:00 and 9:00 pm on 13 February, and a maximum demand value for daily energy of 873 GWh reached on 8 February.
Annual Demand growth (rolling year)
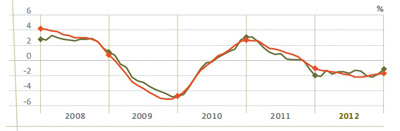
Green line: Uncorrected
Red line: After factoring in the effects of seasonal and working patterns
Renewable energies covered 32% of the demand in 2012, one percentage point less than the previous year.
Wind power increased its contribution to this year's demand coverage by two percentage points reaching a share of 18%, making it the third largest source of electricity behind nuclear, which covered 22% of the demand, and coal, which contributed 20%. Hydroelectric and combined cycle reduced their contribution to 7% and 14%, respectively, and the rest of the other technologies had a similar contribution to that of the previous year.
In addition, the coming into operation of the Spanish Peninsula-Balearic Islands' interconnection has allowed 10% (equating to 569 GWh) of the Balearic Islands' electricity system demand to be covered by the peninsular system.
Annual Demand Coverage 2012 (1) Annual Demand Coverage 2011 (1)
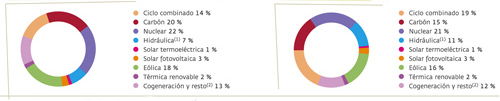
(1) Does not include pumped storage generation. (2) Includes fuel/gas and non-renewable thermal.
Installed power capacity increased by 2,356 MW
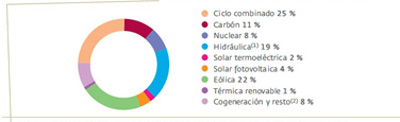
Installed power capacity in the complete set of generating facilities on the peninsula increased by 2,356 MW in 2012, reaching year end with a total of 102,524 MW.
The majority of this variation in power comes from new infrastructures of renewable sources, with 1,122 MW of wind power, 968 MW of solar technologies, 192 MW of hydroelectric and 81 MW of renewable thermal.
Installed power as at 31 December 2012 (102,524 MW)
All-time wind power maximums
Throughout 2012, wind power made a special contribution to the global generation mix, exceeding the maximum values of demand coverage and production. On 24 September, 2012, at 3:03 am, the contribution of wind power exceeded 64% of the coverage of demand on the Spanish peninsula.
In April, wind energy also exceeded the all-time records for instantaneous power, hourly energy and daily energy. On 18 April at 4:41 pm, instantaneous wind production reached 16,636 MW. That same day maximum hourly and daily energy records were also exceeded, with 16,455 MWh and 334,850 MWh, respectively.
Similarly, in November wind power generation was the technology with the largest contribution to the total energy production of the system, reaching 21.3%.
Extra-peninsular systems
Annual demand for electricity in the extra-peninsular systems as a whole grew by 1.0% in 2012 compared with the previous year. By systems, growth was 1.7% in the Balearic Islands, 0.5% in the Canary Islands, 5.5% in Ceuta and 1.4% in Melilla.
The import and export of energy
For the ninth consecutive year, the balance of physical exchanges of electricity was as an exporter with 11,430 GWh, 87.7% higher than in 2011, representing 4.2% of total production on the peninsula. Exports reached 18,857 GWh and imports 7,427 GWh.
Balance of physical international electricity exchanges (GWh)
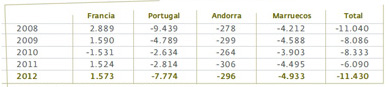
Positive balance: importer; negative balance: exporter
National transmission grid
During 2012, 859.64 km of new lines were put in service, meaning that at the end of the year the national transmission grid totalled 41,369 km of circuit. In addition, transformer capacity rose by 4,830 MVA, increasing the total national transformer capacity to 78,050 MVA.














